In our usage, a social influence network represents an interacting set of individuals and/or institutions that receives an input signal from the landscape or other sources and processes it through interactions among network members to generate a collective output signal. That output signal, in turn, may prompt different actions by those who manage the landscape, for instance through reducing hazardous fuels or deciding whether or not to build new homes in a particular area.
The cycle of receiving a landscape signal, processing it within a network of professionals whose work relates to wildfire risk mitigation, and transmitting the modified output signal to actors who reside in or manage the landscape can thus affect the production of future landscape signals including those related to risk (e.g., potential wildfire or threatened homes) or valued productions (e.g.,timber sales, rare species, sale of new homes).
We abstract these lived human relationships to model social influence networks as a set of nodes and connecting edges. Network nodes represent individuals or institutions involved in influencing a decision. Edges represent pathways of influence propagation. Edge weights represent how effectively a given edge transmits a signal. The network is directional, meaning signals are propagated in one direction along a given edge. Each directional edge has a weight associated with it that indicates the strength with which a signal is transmitted along that edge.
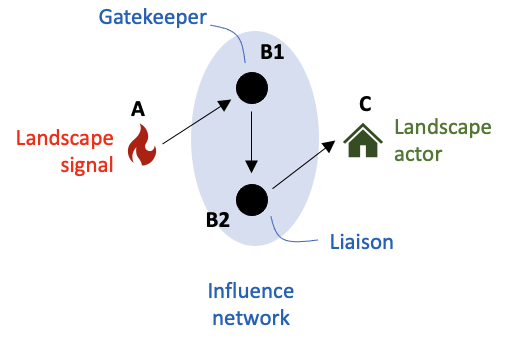
Figure 1. Network influence propagation. A landscape signal from a wildfire is received by a wildfire management network actor (node B1) who serves as a gatekeeper by processing and transmitting the signal to another actor (node B2). This second actor in turn processes the signal they received and, in this case, serves as a liaison to transmit the signal to a landscape actor (node C) who may decide to act differently as a result.
The Social Network Influence Propagation (SNIP) Comparator Tool was developed to allow rapid exploration and pairwise comparison of contrasting social influence networks, and is available as a web application:
The SNIP website includes:
- an overview of social influence network and our approach to simulating them, including details of the SNIP model implementation and steps of model operation
- a SNIP model simulator for exploring and modifying selected networks
- a SNIP model comparator tool for exploring outputs from pairs of networks with different structural characteristics
- a bibliography of relevant literature